To have an edge in the fiercely competitive world of manufacturing, manufacturers must shift production to higher values and advanced technology support and offer a new product-as-a-service model. A 2020 Forbes report states that 47% of all the manufactured products will become smart, connected, and capable of providing a product-as-a-service model.
Top 5 challenges faced by the manufacturing industry
Despite a plethora of opportunities that are integral to the manufacturing industry, specific pain areas need to be addressed soon. Some of them are:
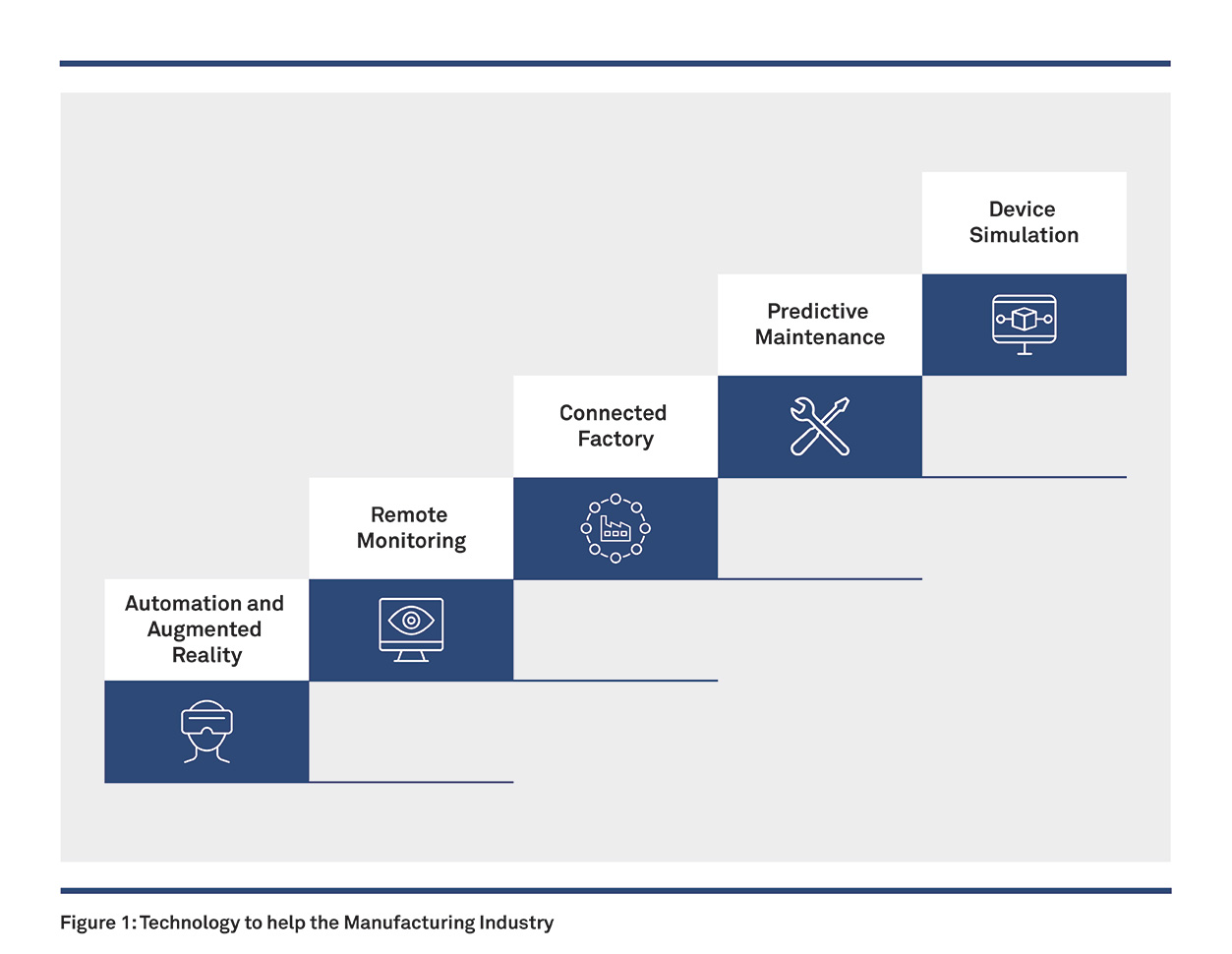
Predictive Maintenance
It is common among businesses to rely on corrective maintenance. Parts are replaced as and when they fail, which causes the factory to shut down. It also impacts product manufacturing, resulting in unhappy customers. At the next level, businesses practice preventive maintenance, determining a part’s lifespan and maintaining or replacing it before a failure. It may cause unnecessary maintenance of machines leading to wastage of money.
Predictive maintenance optimizes the balance between corrective and preventative maintenance by enabling just-in-time replacement of components
The Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance using Azure Serverless Components: Reference Architecture
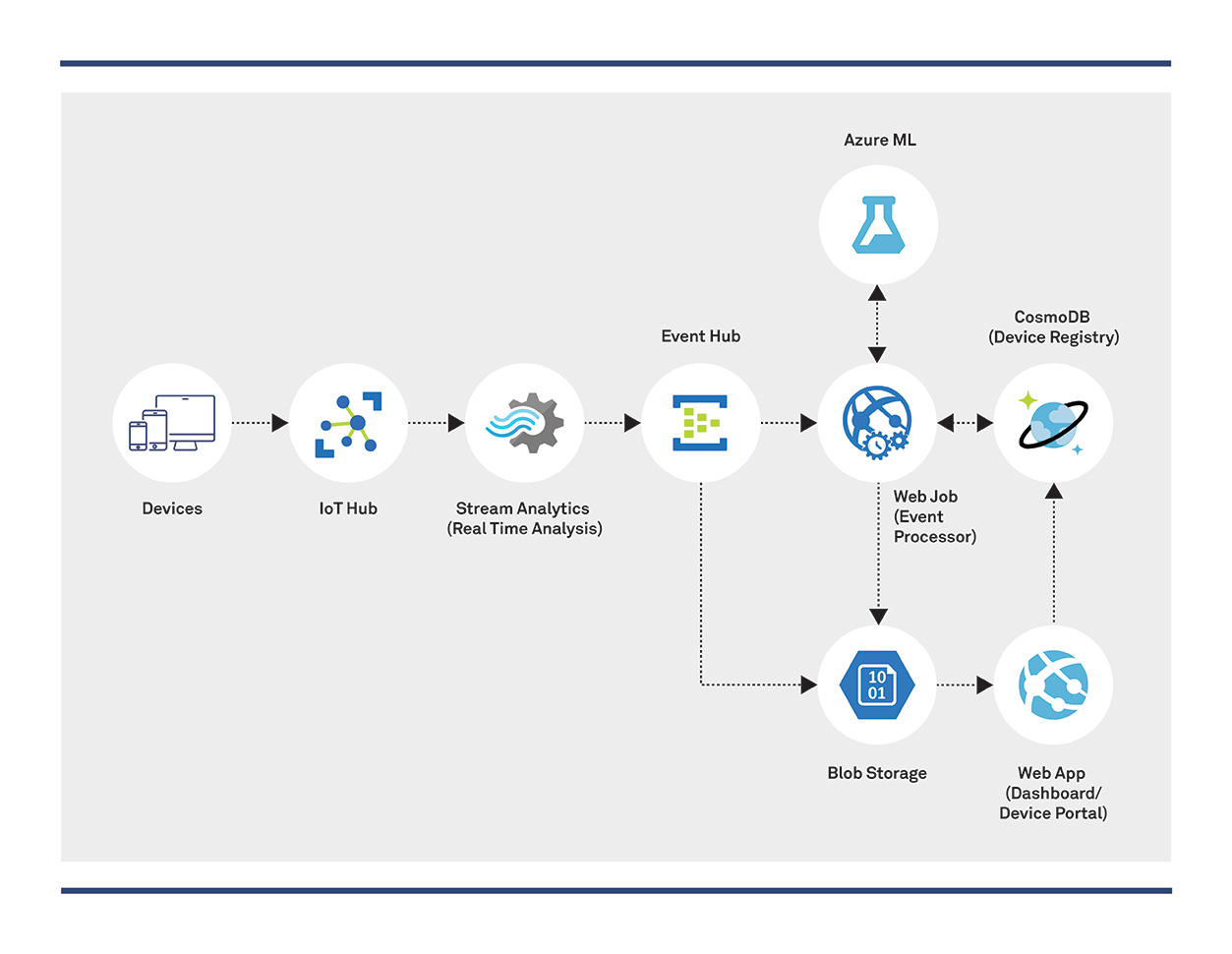
Devices: Devices can be connected to the cloud directly or indirectly. It is done directly using IP-capable devices that establish secure connections via the internet. In the indirect method, devices connect via a field gateway. This enables aggregation and reduced raw device data before transporting the back-end and local decision-making capability.
IoT Hub: Azure IoT Hub offers built-in, high-scale, secure connectivity, data, and event ingestion. It also establishes bi-directional communication with devices, including device management with command and control capabilities. Azure IoT Hub can securely connect millions of devices to the cloud from various devices and protocols.
Stream Analytics: To process the massive amount of data generated by the field devices in real-time and process this live stream, Azure Stream Analytics is used.
Event Hub: Azure Stream Analytics generates an event and sends it to the Event Hub, which triggers background jobs for further analysis.
Event Processor: Web Job is used to process the event data received from Event Hub, and a portion of this data is used to train in the ML model.
Storage: Storage is divided into warm and cold path stores. Warm path data is required to be available for reporting and immediate visualization from devices. Cold path data is stored for the long term and used for batch processing. We use Azure Cosmos DB for warm path storage and Azure Blob for cold path stores.
Dashboard and UI- Web App or Power BI is used to create and show the dashboard to the end-user to engage in interactive browsing.
Machine Learning: It enables systems to learn from historical data and to act without being explicitly programmed. Scenarios such as predictive maintenance are enabled through ML. We use Azure Machine Learning for ML needs.
References:
Alok Bhatnagar
Principal Consultant
Cloud and infrastructure Services
Alok has more than 16 years’ experience in software design, architecture, and development with expertise in cloud-native and cloud-agnostic architecture. He has rich experience working on various cloud platforms like Azure, AWS, and IBM and has leading certifications, including Azure Certified Solution Architect, AWS Certified Solution Architect Associate, and MCSD.